Duodenal Switch
Duodenal Switch is a comprehensive weight loss technique among surgical procedures. It is considered the most effective solution in the treatment of patients who eat high-calorie diets, and it has also been observed to be very effective in conditions such as diabetes, high blood pressure and cholesterol.
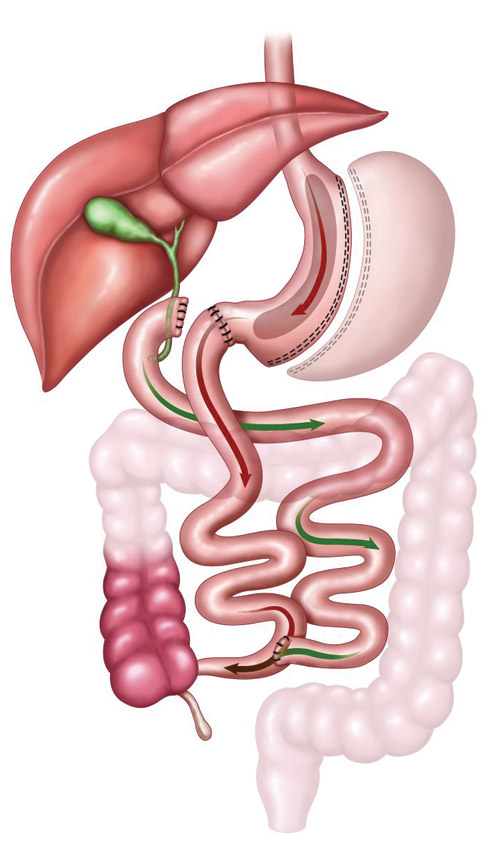
Unlike biliopancreatic diversion surgery, this surgical procedure involves sleeve gastrectomy. During the procedure, the small intestine, which is cut off by protecting the gastric outlet, is anastomosed to the end of the gastric outlet. On the other hand, it reduces a number of side effects observed in biliopancreatic diversion, by ensuring that the joint canal has a length between 75 cm and 10 cm. In addition, the valve of the stomach called the pyloric valve is preserved, so that the patient does not have indigestion problems.
Since the duodenal switch procedure involves the removal of the part of the stomach that produces ghrelin (hunger hormone), the patient’s feeling of hunger decreases, and as a result, the amount of food intake can be limited. Thus, it becomes easier for the patient to lose weight, thanks to the reduced amount of caloric intake after the procedure. Since this procedure intended to reduce the absorption of fat in particular is specific to patients who consume fatty foods, it is observed to be effective in such patients. However, patients who have undergone a duodenal switch operation have to eat a special diet and take vitamin – mineral support throughout their lives.