Endoscopy
Endoscopy is the process of visual examination of hollow organs. Endoscopy is a general name that varies depending on the organ being examined. For example, it is called Gastroscopy in cases where the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum are examined together. Some endoscopists also define this examination as an upper gastrointestinal endoscopy (UGI). In gastroscopy, a flexible device equipped with a camera at the tip called endoscope is inserted into the digestive tract through the mouth, and it is then progressed up to the part called the duodenum. When the endoscopy is performed for the large intestine, it can be called colonoscopy.
However, when endoscopy is mentioned in the society, it usually means gastroscopy performed to monitor the esophagus-stomach-duodenum area.
Since the endoscopic procedures are performed with the sedation method, by creating a conscious sleep state by means of a drug, the patient does not feel discomfort during the procedure. Sedation is not literally putting you to sleep in the operating room. It creates a state of sleep during the procedure so that you do not remember that period. This indicates that the common belief among patients that the procedure is difficult and uncomfortable to perform is wrong.
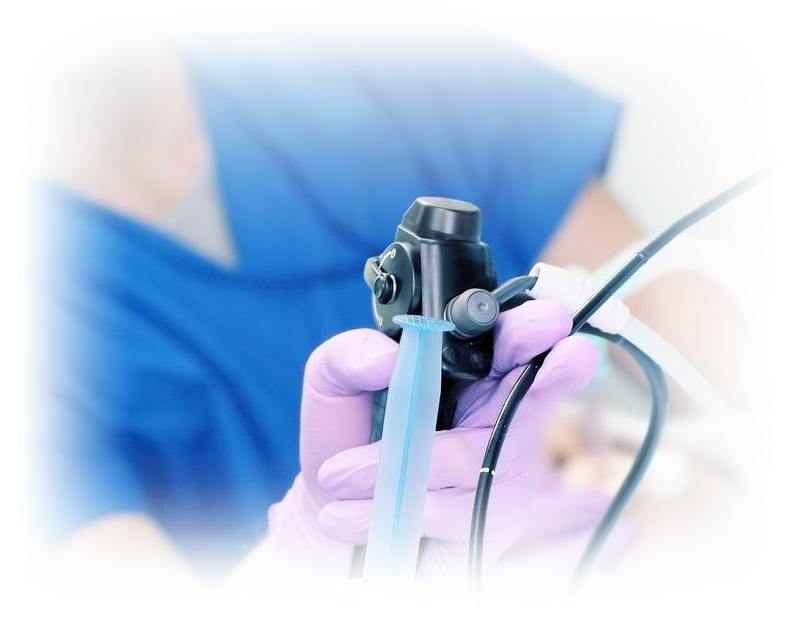
In which situations is gastroscopy performed?
- In the diagnosis of diseases related to the esophagus, such as difficulty in swallowing, burning sensation and pain behind the chest, bitter water coming into the mouth;
- In the diagnosis of diseases related to the stomach and duodenum, such as pain in the upper abdomen, burning sensation, heartburn, nausea, vomiting, treatment-resistant anemia, unexplained weight loss;
- In the detection of bleeding in the upper digestive tract , which manifests itself by fresh blood coming from the mouth, black stool or vomit that resembles coffee grounds in texture;
- In the diagnosis of cancers of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum, as today’s most reliable method;
- In the detection of inflamed areas, ulcers, small tumors;
- With the help of special instruments passed through the gastoscope, it can be used in removing tumors called polyps (fleshy protrusions) with no need for surgery, removing swallowed foreign bodies, and in treatment procedures intended for bleeding control.
In colonoscopy, an instrument called endoscope, which is flexible and longer than the gastroscope, is inserted through the anus and diseases related to the large intestines are investigated at a distance of approximately 70 to 120 cm. Endoscopic examinations of the digestive system, intended for different parts of the digestive system, are performed under different names.
In Which Situations Is Colonoscopy Performed?
- In cases of dark or light-colored blood in the stool, black-colored stool,
- In cases of anemia unresponsive to treatment
- In cases of changes in the form of stool, such as flattening
- In cases of unexplained weight loss or abdominal pain
- In cases of chronic diarrhea or constipation
- For early detection and treatment of intestinal polyps (fleshy protrusions)
- Since colon cancer is a preventable and completely curable type of cancer with early diagnosis, colonoscopy is recommended at the age of 50 and in the following 5-year period even if there is no complaint,
What Is Rectosigmoidoscopy?
The operation of rectosigmoidoscopy is the short version of colonoscopy. Because of its resemblance to the letter S, the last 60 cm section of the large intestine is called the sigmoid colon. The technique intended to examine this part of the large intestine is called rectosigmoidoscopy. Unlike colonoscopy, it does not require preparation a day before the procedure, It is adequate to clean the bowels with the administration of an enema in the hospital.
The procedure takes about 5 minutes. It is usually performed under the effect of a mild relaxing drug, also depending on the patient’s choice. As in the colonoscopy procedure, biopsy can be taken if needed, or a polypectomy (removal of the polyp) can be performed if there is any polyp. It is recommended for young patients with bleeding accompanied by the complaints of a typical hemorrhoidal or fissure (crack, tear).

Legal warning
This website is not intended to provide medical services, but to give information about the treatment procedures that we perform. The information available on the website has not been provided for use in the diagnosis or treatment of diseases. The responsibility arising from the use of the information in our website content for the purpose of diagnosis and treatment belongs to the visitors of the website.
Contact
Address: Küçükbakkalköy, QBMED Plaza, Işıklar Cd. No:37, 34750 Ataşehir/İstanbul
Phone: +90 (532) 228 33 60
Working Hours:Weekdays: 09:00 – 17:00, Saturday: 09:00 – 13:00
